Describe Atp Synthase and Its Role
Science Biology QA Library Describe in detail the role of ATP synthase in the thylakoid membrane. Discuss the source fate and flow of electrons and energy in.

Atp Synthase Definition Structure Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Modification of work by Klaus Hoffmeier Dinitrophenol DNP is an uncoupler that makes the inner mitochondrial membrane leaky to protons.
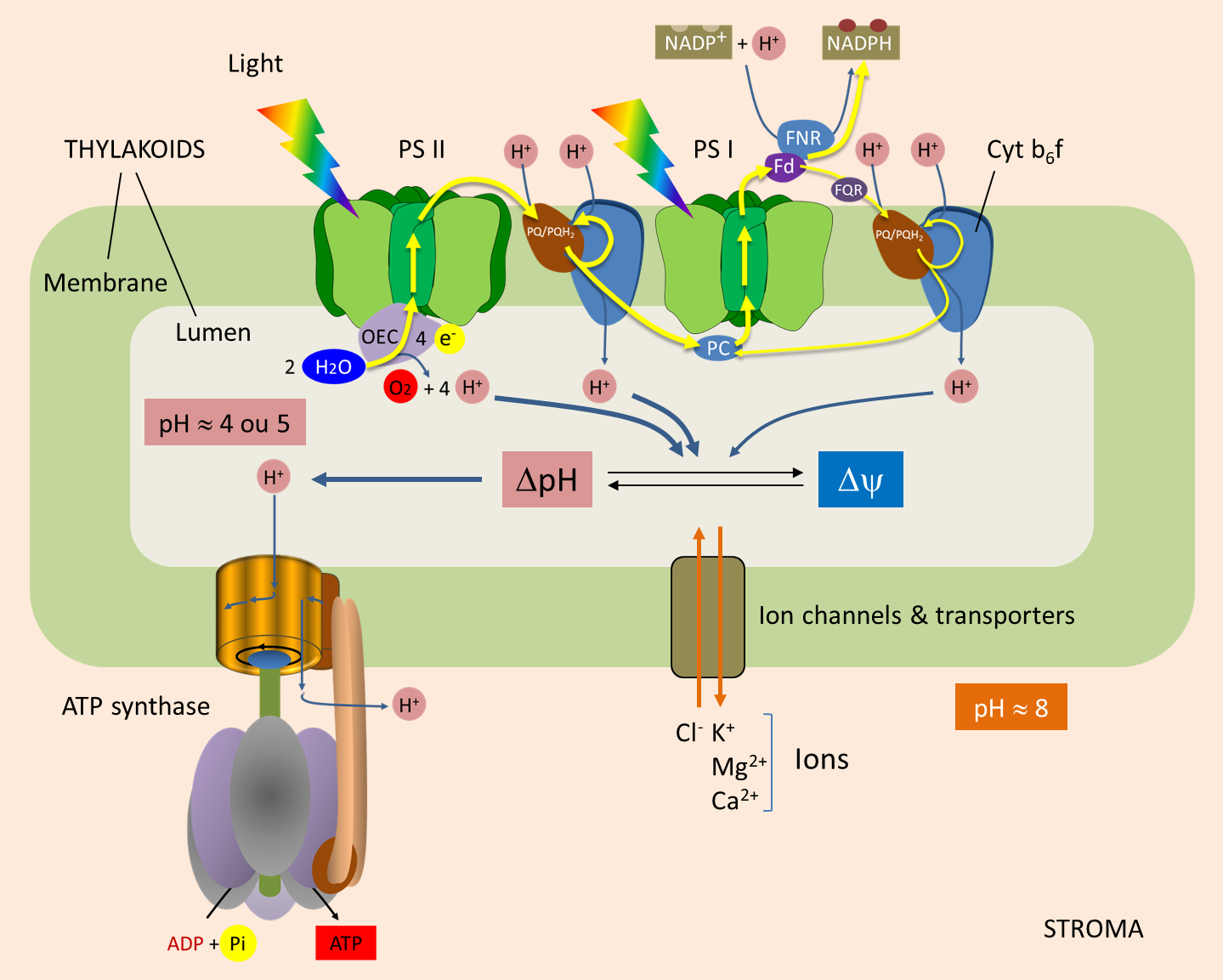
. ATP synthase is a transmembrane enzyme complex which catalyses the generation of ATP through the condensation of ADP plus Pi. Energy from ATP is released when the molecule loses a phosphate group which thus forms ADP. And ATP synthase provides a channel for those protons.
Autoantibodies Second Edition 2007 Download as PDF About this page. What is the role of the proteins ATP synthase. The ATP synthase is a mitochondrial enzyme localized in the inner membrane where it catalyzes the synthesis of ATP from ADP and phosphate driven by a flux of protons across a gradient generated by electron transfer from the proton chemically positive to the negative side.
ATP synthase is a complex structure consisting of two domains F O and F 1. ATP synthase is a protein that synthesizes adenosine diphosphate ADP and an extra phosphate together into adenosine triphosphate ATP. Chapter 10 flashcards 35 terms.
It is classified under ligases as it changes ADP by the formation of P-O bond phosphodiester bond. In photosynthesis after being synthesized by photophosphorylation in the light-dependent reactions the role of ATP together with NADPH is to provide the energy needed for glucose synthesis in the light-independent reactions aka. ATP synthase Click card to see definition Enzyme that synthesizes ATP.
As a result of these light-induced reactions energy becomes chemical. This chapter describes the structure and function of ATP synthase. ATP synthase is a protein that catalyzes the formation of the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate ATP using adenosine diphosphate ADP and inorganic phosphate P i.
The molecule is pertinent for cellular operations to occur. Click again to see term 126 THIS SET IS OFTEN IN FOLDERS WITH. An enzyme is a protein that helps biochemical reactions occur.
ATP synthase is an enzyme that directly generates adenosine triphosphate ATP during the process of cellular respiration. Substrate level phosphorylation is that ATP synthesis occurs whan an enzyme directly transfer phosphate group from a substrate molecule to ADP. Eg 13 bisphosphoglycerate to 3 phosphoglycerate yield ATP directly by.
ATP synthase is a complex molecular machine that uses a proton H gradient to form ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate Pi. The mitochondrial H -ATP synthase is a primary hub of cellular homeostasis by providing the energy required to sustain cellular activity and regulating the production of signaling molecules that reprogram nuclear activity needed for adaption to changing cues. ATP synthase is an enzyme located in the mitochondria and chloroplasts plant cells that produces the energy currency of the cell known as adenosine triphosphate ATP.
ADP and ATP play an integral role in the production and use of energy. The function of ATP synthase is to synthesize ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate P i in the F 1 sector. F 1 is a spherical structure sticks out into the matrix and is anchored to the membrane consists of three α- and three β- subunits all of which can bind nucleotides but only the β-subunits can take part in the reactions Fig.
The process is then recycled back to ATP with the help of ATP synthase as the ADP molecule passes through the mitochondria. ATP synthase is a membrane protein which converts the proton gradient across membrane into energy storing molecule ATP important for biological purposes. What Is Light Dependant Reaction In Photosynthesis.
ATP synthase is a molecular machine. ATP synthase brings out the formation of ATP at the time of light-reaction photosynthesis. ATP synthase is an enzyme that synthesizes adenosine triphosphate ATP in the mitochondrial inner membrane.
Its primary role is to produce high energy ATP molecule. ATP is mainly produced in the mitochondria and is an important enzyme that provides energy for the cell to use through the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate ATP. Light reactions of photosynthesis which are based on light energy to produceATP and NADPH from water.
This is possible due to energy derived from a gradient of protons which cross the inner mitochondrial membrane from the intermembrane space into the matrix through the F o portion of the enzyme. ATP is used by most all. But as those protons travel through the ATP synthase they turn this part of it which drives this axle and then this axle nudges these parts of the protein so that they jam together an ADP with a phosphate group to produce ATP.
For a simplified visualization of how Continue Reading. All ATP-synthase complexes producing great amounts of ATP in living organisms are coupled to chains of electron transporters integrated in. Chemomechanical coupling has been studied extensively for.
ATP is the principal. -ATP synthase is located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria Function-ATP synthase combines with ADP in order to form ATP-ATP is needed to power all cellular processes-ATP synthase function is to produce ATP. It was used until 1938 as a weight-loss drug.
Discuss the source fate and flow of electrons and energy in detail naming all molecules. ATP synthase forms ATP from adenosine diphosphate ADP and an inorganic phosphate Pi through oxidative phosphorylation which is a process in which enzymes oxidize nutrients to form ATP. The rotary motor enzyme F1-ATPase F1 is a catalytic subcomplex of FoF1-ATP synthase that produces most of the ATP in respiring cells.
ATP is synthesized through oxidative phosphorylations by an ATP-synthase complex coupled to the respiratory chain. ATP synthase uses the intermembrane space in order to convert protons and generate a type of nuclear energy.

Question Video Describing The Role Of Atp Synthase In Oxidative Phosphorylation Nagwa

Oxidative Phosphorylation Structure And Function Of Atp Synthase Mitochondrial Transport Systems And Inhibitors Of Ox Phos Bioc 460 Spring Lecture Ppt Download
No comments for "Describe Atp Synthase and Its Role"
Post a Comment